Anemia, a condition marked by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the body, can result from various factors. Three primary reasons include a lack of iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12. To address this deficiency, incorporating specific foods into your diet can significantly improve blood levels.
Physiological effects of Anemia on the Human Body
A deficiency of hemoglobin in the blood leads to reduced oxygen transport to tissues, causing fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Other symptoms may include pale skin, dizziness, and cold hands/feet. Severe anemia can affect the heart, leading to an increased heart rate or heart palpitations. It's important to identify the underlying cause and address it, as anemia can result from various factors such as nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, or genetic conditions.
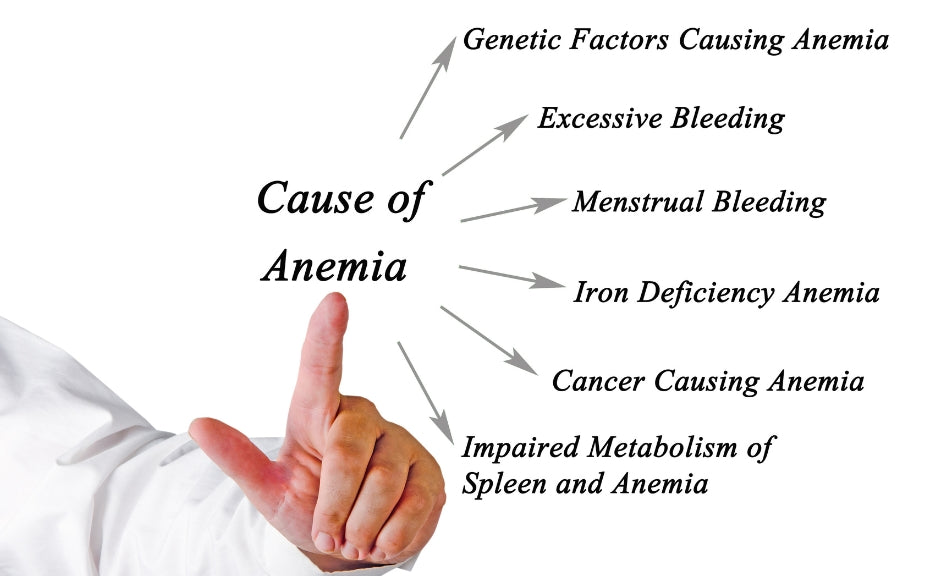
Anemia can result from various factors, each affecting the body's ability to produce an adequate number of healthy red blood cells. Here are some key causes:
Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Iron Deficiency: Insufficient iron intake or poor absorption can hinder the production of hemoglobin, leading to iron-deficiency anemia.
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Lack of B12, crucial for red blood cell formation, can cause pernicious anemia.
Chronic Diseases:
- Chronic Inflammation: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or chronic kidney disease can disrupt red blood cell production.
- Chronic Infections: Persistent infections, such as HIV or tuberculosis, may contribute to anemia.
Genetic Factors:
- Sickle Cell Anemia: An inherited disorder causing abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in misshapen red blood cells and reduced oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Thalassemia: Genetic mutations affecting hemoglobin synthesis, leading to anemia.
Hemolysis:
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: The immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys red blood cells.
- Hereditary Spherocytosis: A genetic disorder causing spherical-shaped red blood cells prone to premature destruction.
Bone Marrow Disorders:
- Aplastic Anemia: Damage to the bone marrow, often due to toxins, radiation, or certain medications, impairs blood cell production.
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Abnormal bone marrow function hampers the production of healthy blood cells.
Medical Treatments:
- Chemotherapy: Cancer treatments can suppress bone marrow activity, leading to anemia.
- Certain Medications: Some drugs may interfere with red blood cell production or trigger immune reactions.
Dietary Choices:
- Vegetarianism/Veganism: Limited intake of iron-rich foods in plant-based diets can contribute to anemia.
- Malabsorption: Conditions like celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease may hinder nutrient absorption.
Hemorrhage:
- Acute Blood Loss: Trauma, surgery, or gastrointestinal bleeding can rapidly reduce red blood cell levels, causing acute anemia.
Understanding these diverse causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment of anemia. It's essential to consult with healthcare professionals for proper evaluation and management based on the specific underlying cause.
How Can We Increase Hemoglobin Levels?
Green Vegetables: Include a variety of green vegetables in your diet, emphasizing those suitable for the current weather.
Banana: Eat three bananas in the morning, mixed with sugar candy and cardamom in milk. This combination serves as a nutritious snack that helps alleviate blood deficiency.
Grapes: Consuming 10 ounces of grape juice provides relief from anemia, effectively replenishing blood levels.
Lemon and Tomato Juice: Individuals with low blood levels can benefit from regular consumption of lemon and tomato juice, aiding in preventing a gradual decline in the body.
Amla: Prepare a mixture of two teaspoons of honey and half a cup of amla juice, drinking it to boost blood levels.
Phalsa: Eating Phalsa is known to increase blood in the body.
Carrot and Spinach Juice: Mix 250 grams of carrot juice with spinach juice and consume regularly to enhance blood levels.
Beetroot: Regular consumption of beetroot is highly beneficial in increasing blood and is often referred to as "pure blood" by doctors.
Onion: The iron-rich content in onions makes them effective in addressing blood deficiency. Various combinations of onion juice, carrot juice, amla juice, spinach juice, and tomato juice can be consumed for maximum benefits.
Pomegranate: Regular consumption of pomegranate helps overcome blood deficiency and contributes to a healthy complexion.
Honey: Drinking one teaspoon of honey in water or milk three times a day is recommended for those experiencing blood deficiency.
Spinach: Both spinach vegetables and spinach juice are excellent for increasing blood levels. Adding honey to spinach juice not only enhances its taste but also contributes to improved facial complexion, increased energy, and faster blood circulation.
Blood-Enhancing Dry Grapes: Soak 60 grams of dry grapes for twelve hours and consume them to gradually increase blood levels. Eating three to four kilos of soaked dry grapes annually is considered highly beneficial.
Bael: Grind the dry pulp of the bael fruit, mix two teaspoons with hot milk, and add powdered sugar candy according to taste. This serves as a potent blood-boosting tonic.
Incorporating these foods into your daily routine can effectively combat anemia, leading to improved overall health. From green vegetables and fruits like bananas, grapes, and pomegranates to the nutritional powerhouse of honey and the blood-boosting properties of dry grapes and bael, these dietary choices can make a significant impact on your blood levels. Regular consumption of these natural remedies, coupled with a balanced diet, can help address anemia and promote a healthier, more vibrant lifestyle.
Other Ways of Treating Anemia:
Vitamin B complex, folic acid, ferrous fumarate, vitamin B12, and minerals play crucial roles in treating anemia.
- Vitamin B Complex: Essential for red blood cell production and overall energy metabolism.
- Folic Acid: Aids in DNA synthesis and is particularly important during periods of rapid cell division, such as in red blood cell formation.
- Ferrous Fumarate: A source of iron, which is vital for hemoglobin production, helping transport oxygen in the blood.
-
Vitamin B12: Necessary for the maturation of red blood cells and the maintenance of the nervous system.
Minerals play a crucial role in treating anemia, a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin. Iron is a key mineral involved in the production of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood. Adequate iron intake helps combat iron-deficiency anemia, the most common type of anemia. Other minerals, such as vitamin B12 and folate, are also essential for red blood cell formation. Including a variety of mineral-rich foods in your diet or taking supplements under medical guidance can support the treatment of anemia. These components work synergistically to address different aspects of anemia, ensuring proper red blood cell development and function.
Conclusion
You can also try Fytika Vita – 365. To treat Anemia, it contains multi-vitamins, multi-minerals, folic acid, vitamin B12, ferrous fumarate along with Ashwagandha, Ginseng Extract, and Grape Seeds Extracts. These ingredients help in treating anemia.